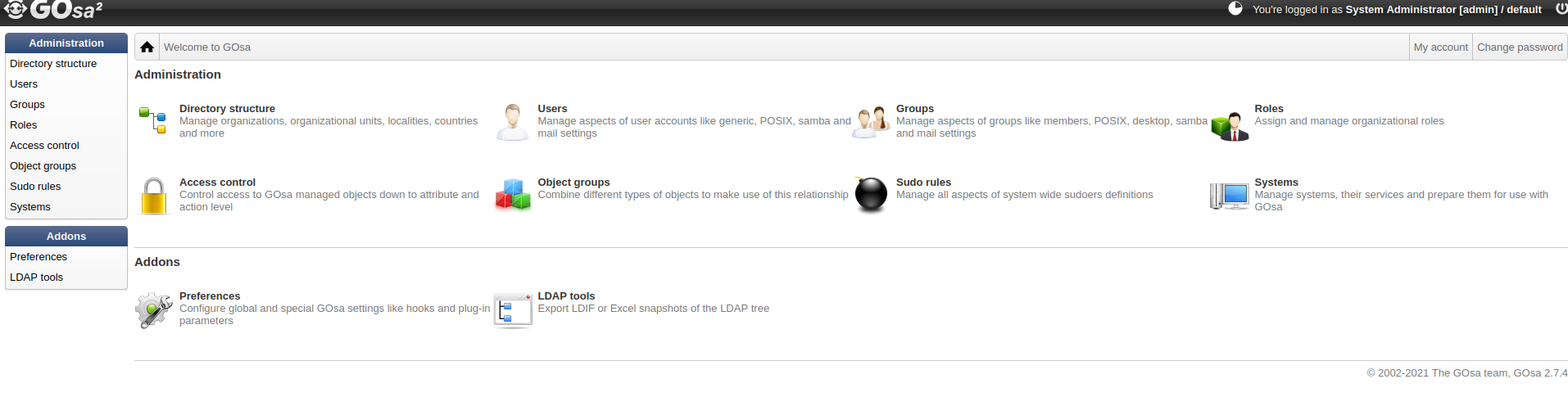
Installing GOsa web interface on top of OpenLDAP
Sometimes
you need to manage your user directory in a comfortable way just not to create/dig around with complex ldif styled files. To make your life a bit easier for such cases this short tutorial will guide you through the installation of GOsa web interface on top of our ldap service.
All steps will be done on a plain debian buster installation.
Update the system
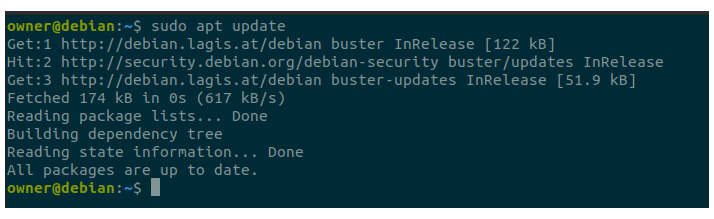
Just ssh into you machine and update your cache
$ sudo apt update$ sudo apt install gosa gosa-schema gosa-plugin-ssh gosa-plugin-ssh-schema gosa-plugin-sudo gosa-plugin-sudo-schema gosa-plugin-systems gosa-plugin-rolemanagement gosa-plugin-ldapmanager gosa-plugin-mailWith listed above packages, Apache webserver and PHP packages are installed automatically as they are required to run GOsa.
Check the services status
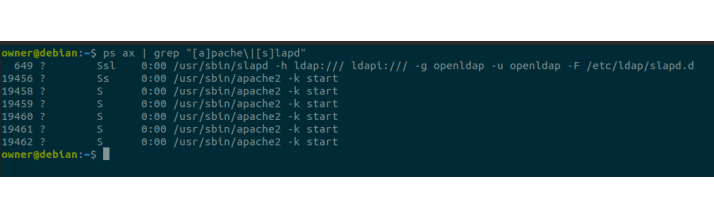
Ensure that openLDAP and Apache services are up and running
ps ax | grep "[a]pache\|[s]lapd"Configure apache server
Next, copy /etc/gosa/gosa-apache.conf into /etc/apache2/sites-available/ as gosa.conf
sudo cp /etc/gosa/gosa-apache.conf /etc/apache2/sites-available/gosa.confLet's adjust gosa.conf so that it looks like that:
<IfModule mod_php7.c>
<VirtualHost _default_:80>
DocumentRoot /usr/share/gosa/html
<Location />
php_admin_flag engine on
php_admin_flag register_globals off
php_admin_flag allow_call_time_pass_reference off
php_admin_flag expose_php off
php_admin_flag zend.ze1_compatibility_mode off
php_admin_flag register_long_arrays off
php_admin_flag magic_quotes_gpc off
php_admin_value upload_tmp_dir /var/spool/gosa/
php_admin_value session.cookie_lifetime 0
include /etc/gosa/gosa.secrets
</Location>
</VirtualHost>
</IfModule>After your editing you have two options:
- Make a link under /etc/apache/sites-enabled/gosa.conf pointing to /etc/apache/sites-available/gosa.conf
sudo ln -s /etc/apache2/sites-available/gosa.conf /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/gosa.confand restart apache
sudo systemctl restart apache2or - use built-in mechanism of apache:
$ sudo a2ensite gosa $ sudo systemctl restart apache2
Configure gosa
So, you are almost ready to go, just navigate to http://<server-ip-address> in your browser and ensure that you see the setup welcome page of GOsa.
There, on the welcome page you will also see what to do next. Just follow the instructions on the screen.
Steps are:
- writing a string to a file
- stopping apache web service
- replacing parameter in the systemd file, to disable private temporary directory for apache service
- reloading the systemd daemon, to activate the changes
- starting apache service again
echo -n l0ngstr1ngxxxxxxxxxxxx > /tmp/gosa.auth
sudo service apache2 stop
sudo sed -i 's/Tmp=true/Tmp=false/' /lib/systemd/system/apache2.service
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo service apache2 startAfter this actions click Next
revert the change made above, just to be on the secure side
sudo service apache2 stop
sudo sed -i 's/Tmp=false/Tmp=true/' /lib/systemd/system/apache2.service
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
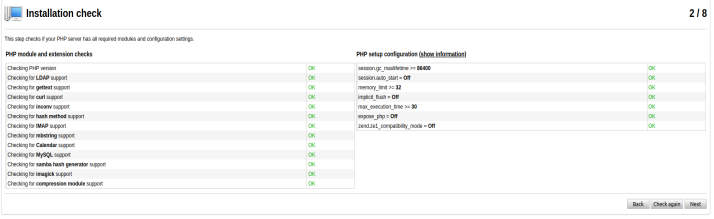
sudo service apache2 startOn the second step system ensures you have everything installed.
Just push Next button.
On the third step you need to accept the license otherwise you would not be able to finish the installation.
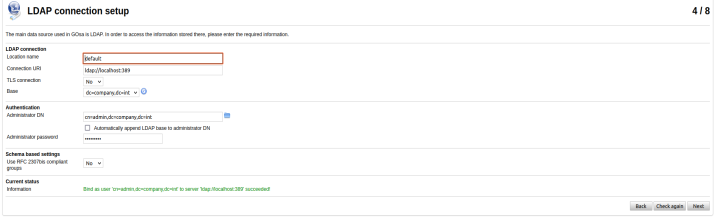
Fourth step. Here it comes to configuration of GOsa web interface, how it can communicate to the OpenLDAP server.
As we previously installed ldap service on the same server as gosa, we need to specify the same admin credentials, which we used while configuring ldap server. Click on the button "Check again" and ensure, that credentials are correct. You will see the green message in the bottom. Click Next
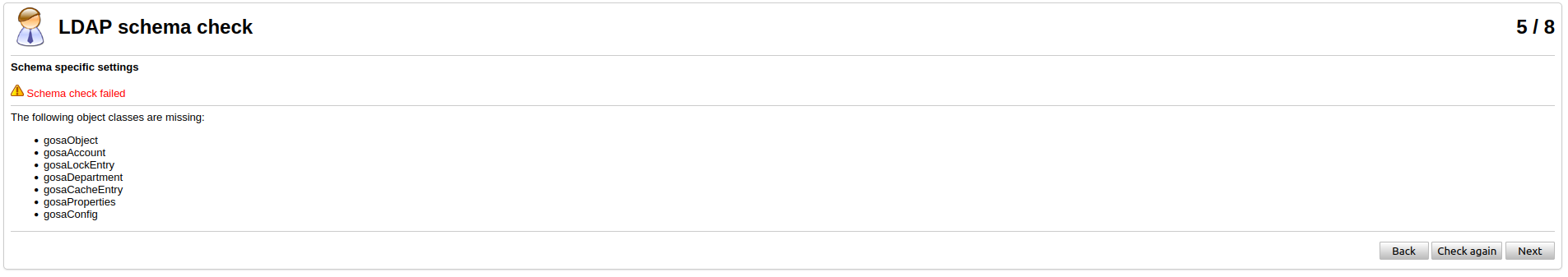
On the next step you will get the message about missing schema, which we need to install.
Install them by running:
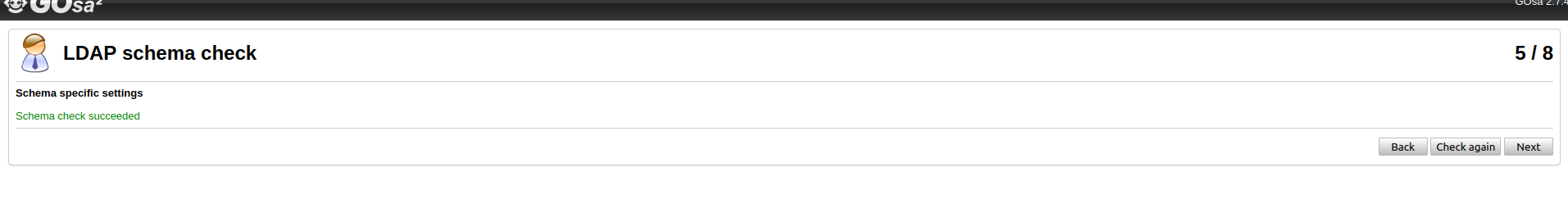
for i in /etc/ldap/schema/gosa/*.ldif; do sudo ldapadd -Y EXTERNAL -H ldapi:/// -f $i; doneAnd recheck the configuration again by clicking on "Check again". You will get the success message.
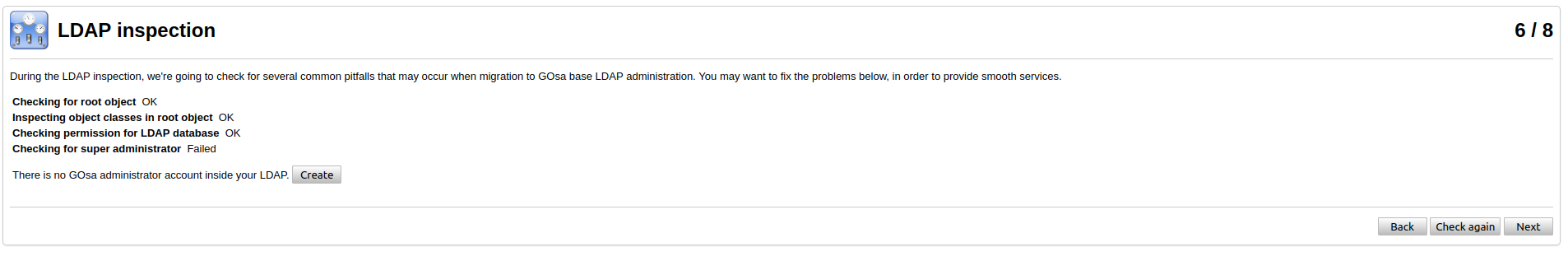
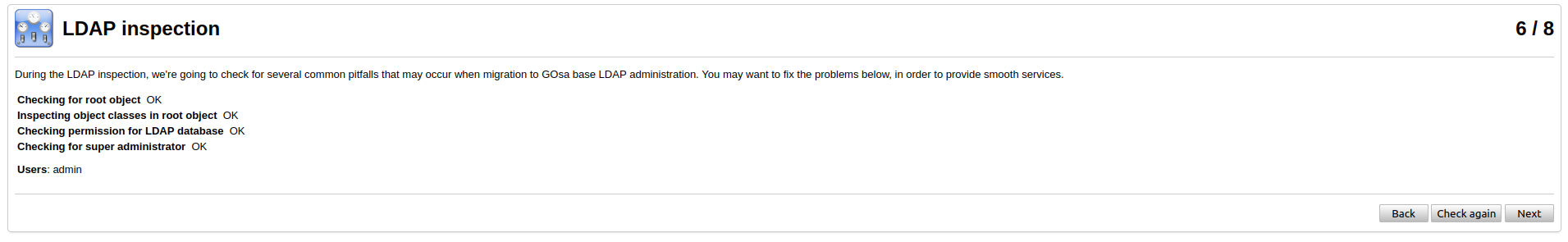
On the next step you need to migrate the ldap database and create gosa admin.
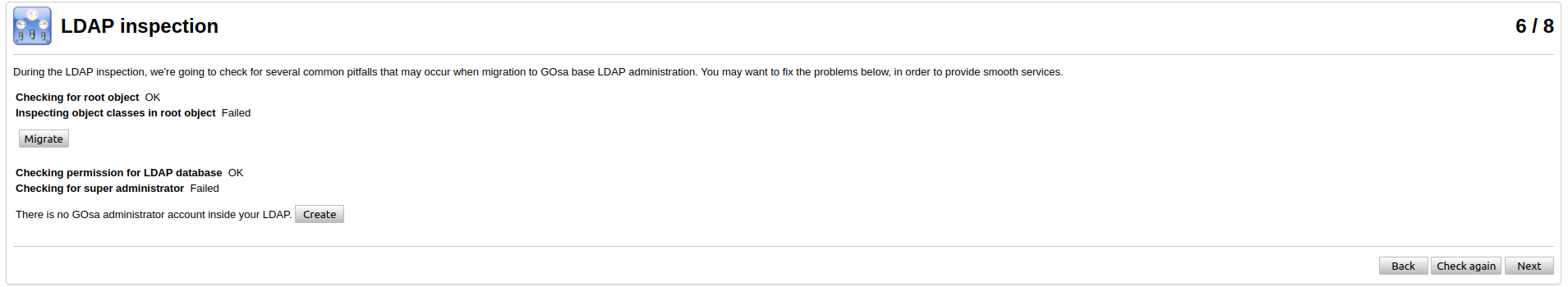
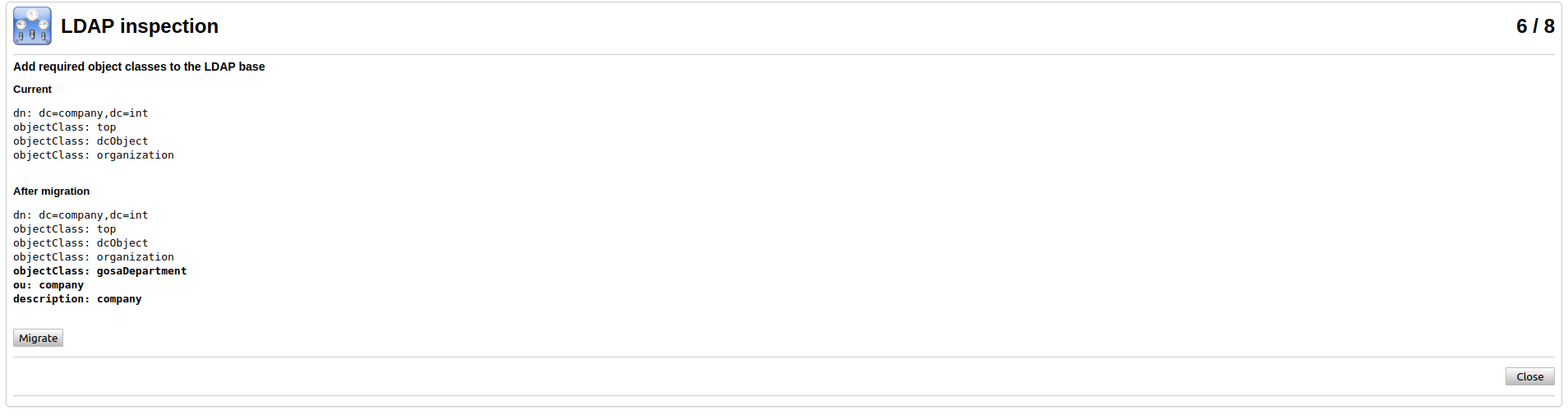
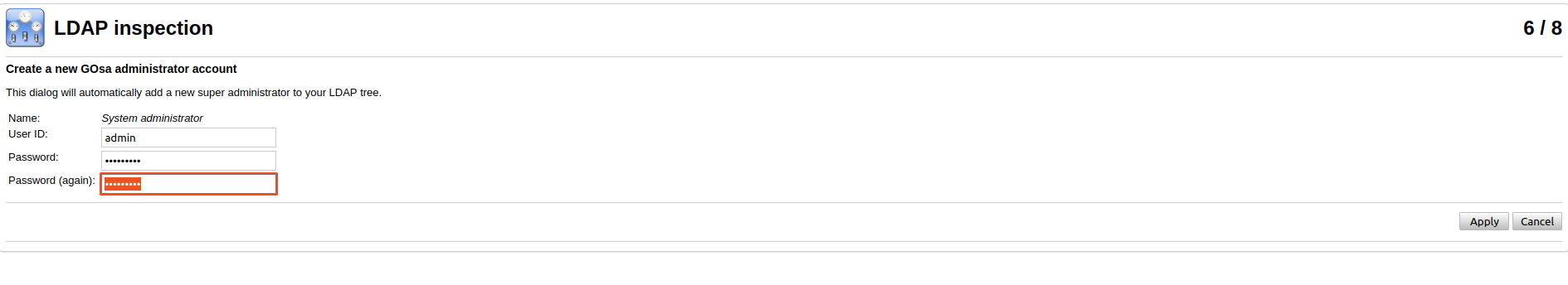
After you created admin account the 7th step could be skipped, if you want.
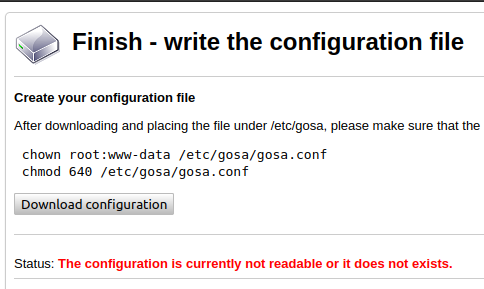
Download the config file and put it under /etc/gosa/
Change the owner of that to root:www-data so that web server can read it and change the permissions to 0640
sudo chown :www-data /etc/gosa/gosa.conf
sudo chmod 0640 /etc/gosa/gosa.confReturn to browser and click Check again, then Next
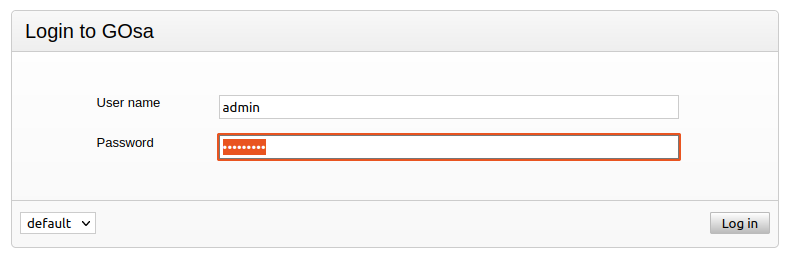
Navigate to http://_<server-ip-address>_ and login with your gosa admin account and the password specified earlier.
That's it, gosa is configured and can be used to manage your user, groups and systems.